Introduction to Lists
Todo, agendas, names, phone numbers - all the information you need in one place!
What is a list?
A list is a collection of data in an ordered list.
Examples of Lists
- Names of people in your address book
- Important telephone numbers
- To-do list
Declaring a List
Declaring a list is simple - just enclose your list in brackets and separate each element with comma.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']

Elements in a List
Lists store data in a sequential manner, every element has a number which tells us its position in a list.
- This number is called an index (singular) or indices (plural).
- Indices in computer science generally start from the number 0.
- You can start from the end of the list and go backwards by using the index -1 and decreasing the index.
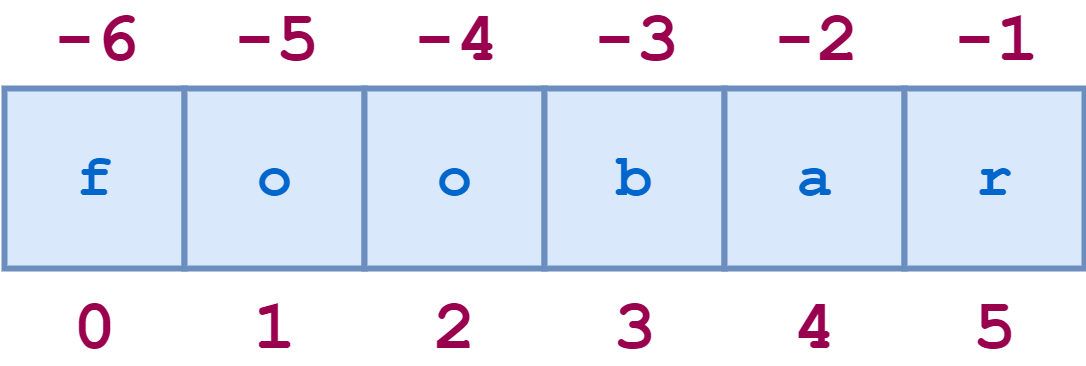

Accessing Elements in a List
Python gives us a simple way to access any element in a list given the index
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
print(shows[1])
print(shows[1].upper())
print(shows[-1].upper())
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> Arrested Development
> ARRESTED DEVELOPMENT
> BREAKING BAD
Line 4 shows that you can also call methods such as
.upper() after accessing
the element.

Using Values Stored in a List
You can use an element stored in a list by accessing its index and using f-strings .
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(f"My favorite show is {shows[1]}, I heard your favorite show is {shows[3]}.")
> My favorite show is Arrested Development, I heard your favorite show is Breaking Bad.
Modifying Values in a List
Modifying a value from a list is very easy - just supply the index and assign it a new value.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Change the third element of the list.
shows[2] = 'Clifford'
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'Clifford', 'Breaking Bad']

Adding New Elements to the end of a List
Elements can be added to the end of a list by using
the append() method on
a list.
This is great because you do not need to know the length of the list to add a new element at the end.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Add an element to the end of the list
shows.append('Curious George')
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad', 'Curious George']
Adding Elements to a Specific Index
You can add an element to a specific position in the list by using
the insert() method.
list.insert(index,value)
This causes your element to be added at the specified index and it shifts all other elements to the right one index.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Add an element to index 1
shows.insert(1,'NCIS')
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> ['DBZ', 'NCIS', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']

Removing Elements from a List
The del command
You can remove any element from a list using the
del command.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Delete the 3rd element
del shows[2]
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'Breaking Bad']
The pop() method
If you would like to have delete and element and have access to
its value you can use the
pop() method.
If you call the method without an argument its default behavior is to pop the last element in a list.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Pop the last element and print it to a string.
print(f'My favorite show is {shows.pop()}.')
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> My favorite show is Breaking Bad.
['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons']
Popping a specific element
Supplying an index number to the pop command allows you to choose which element you pop.
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Pop the last element and print it to a string.
print(f'My favorite show is {shows.pop(1)}.')
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> My favorite show is Arrested Development.
['DBZ', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']

Removing Elements by Value
Instead of removing and element by its index, you can instead
search for a specific value, x, and remove it using the
remove(x)
method
shows = ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
print(shows)
# Remove the first occurence of 'The Simpsons'
shows.remove('The Simpsons')
print(shows)
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'The Simpsons', 'Breaking Bad']
> ['DBZ', 'Arrested Development', 'Breaking Bad']
